HBLbits_Verilog Basic_Lfsr5
A linear feedback shift register is a shift register usually with a few XOR gates to produce the next state of the shift register. A Galois LFSR is one particular arrangement where bit positions with a "tap" are XORed with the output bit to produce its next value, while bit positions without a tap shift. If the taps positions are carefully chosen, the LFSR can be made to be "maximum-length". A maximum-length LFSR of n bits cycles through 2n-1 states before repeating (the all-zero state is never reached).
The following diagram shows a 5-bit maximal-length Galois LFSR with taps at bit positions 5 and 3. (Tap positions are usually numbered starting from 1). Note that I drew the XOR gate at position 5 for consistency, but one of the XOR gate inputs is 0.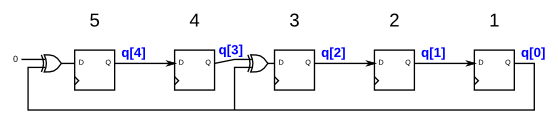
Build this LFSR. The reset should reset the LFSR to 1.
module top_module(
input clk,
input reset, // Active-high synchronous reset to 5'h1
output [4:0] q
);
reg [4:0] q_next; // q_next is not a register
always @(*) begin
q_next = q[4:1]; // Shift all the bits. This is incorrect for q_next[4] and q_next[2]
q_next[4] = q[0]; // Give q_next[4] and q_next[2] their correct assignments
q_next[2] = q[3] ^ q[0];
end
always @(posedge clk) begin
if (reset)
q <= 5'h1;
else
q <= q_next;
end
endmodule
module top_module(
input clk,
input reset, // Active-high synchronous reset to 5'h1
output [4:0] q
);
always @(posedge clk) begin
if (reset)
q <= 5'h1;
else
q <= {q[0],q[4],q[3]^q[0],q[2],q[1]};
end
endmodule
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// File downloaded from http://www.nandland.com///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// Description: // A LFSR or Linear Feedback Shift Register is a quick and easy way to generate// pseudo-random data inside of an FPGA. The LFSR can be used for things like// counters, test patterns, scrambling of data, and others. This module// creates an LFSR whose width gets set by a parameter. The o_LFSR_Done will// pulse once all combinations of the LFSR are complete. The number of clock// cycles that it takes o_LFSR_Done to pulse is equal to 2^g_Num_Bits-1. For// example setting g_Num_Bits to 5 means that o_LFSR_Done will pulse every// 2^5-1 = 31 clock cycles. o_LFSR_Data will change on each clock cycle that// the module is enabled, which can be used if desired.//// Parameters:// NUM_BITS - Set to the integer number of bits wide to create your LFSR.///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////module LFSR #(parameter NUM_BITS) ( input i_Clk, input i_Enable, // Optional Seed Value input i_Seed_DV, input [NUM_BITS-1:0] i_Seed_Data, output [NUM_BITS-1:0] o_LFSR_Data, output o_LFSR_Done ); reg [NUM_BITS:1] r_LFSR = 0; reg r_XNOR; // Purpose: Load up LFSR with Seed if Data Valid (DV) pulse is detected. // Othewise just run LFSR when enabled. always @(posedge i_Clk) begin if (i_Enable == 1'b1) begin if (i_Seed_DV == 1'b1) r_LFSR <= i_Seed_Data; else r_LFSR <= {r_LFSR[NUM_BITS-1:1], r_XNOR}; end end // Create Feedback Polynomials. Based on Application Note: always @(*) begin case (NUM_BITS) 3: begin r_XNOR = r_LFSR[3] ^~ r_LFSR[2]; end 4: begin r_XNOR = r_LFSR[4] ^~ r_LFSR[3]; end 5: begin r_XNOR = r_LFSR[5] ^~ r_LFSR[3]; end 6: begin r_XNOR = r_LFSR[6] ^~ r_LFSR[5]; end 7: begin r_XNOR = r_LFSR[7] ^~ r_LFSR[6]; end 8: begin r_XNOR = r_LFSR[8] ^~ r_LFSR[6] ^~ r_LFSR[5] ^~ r_LFSR[4]; end 9: begin r_XNOR = r_LFSR[9] ^~ r_LFSR[5]; end 10: begin r_XNOR = r_LFSR[10] ^~ r_LFSR[7]; end 11: begin r_XNOR = r_LFSR[11] ^~ r_LFSR[9]; end 12: begin r_XNOR = r_LFSR[12] ^~ r_LFSR[6] ^~ r_LFSR[4] ^~ r_LFSR[1]; end 13: begin r_XNOR = r_LFSR[13] ^~ r_LFSR[4] ^~ r_LFSR[3] ^~ r_LFSR[1]; end 14: begin r_XNOR = r_LFSR[14] ^~ r_LFSR[5] ^~ r_LFSR[3] ^~ r_LFSR[1]; end 15: begin r_XNOR = r_LFSR[15] ^~ r_LFSR[14]; end 16: begin r_XNOR = r_LFSR[16] ^~ r_LFSR[15] ^~ r_LFSR[13] ^~ r_LFSR[4]; end 17: begin r_XNOR = r_LFSR[17] ^~ r_LFSR[14]; end 18: begin r_XNOR = r_LFSR[18] ^~ r_LFSR[11]; end 19: begin r_XNOR = r_LFSR[19] ^~ r_LFSR[6] ^~ r_LFSR[2] ^~ r_LFSR[1]; end 20: begin r_XNOR = r_LFSR[20] ^~ r_LFSR[17]; end 21: begin r_XNOR = r_LFSR[21] ^~ r_LFSR[19]; end 22: begin r_XNOR = r_LFSR[22] ^~ r_LFSR[21]; end 23: begin r_XNOR = r_LFSR[23] ^~ r_LFSR[18]; end 24: begin r_XNOR = r_LFSR[24] ^~ r_LFSR[23] ^~ r_LFSR[22] ^~ r_LFSR[17]; end 25: begin r_XNOR = r_LFSR[25] ^~ r_LFSR[22]; end 26: begin r_XNOR = r_LFSR[26] ^~ r_LFSR[6] ^~ r_LFSR[2] ^~ r_LFSR[1]; end 27: begin r_XNOR = r_LFSR[27] ^~ r_LFSR[5] ^~ r_LFSR[2] ^~ r_LFSR[1]; end 28: begin r_XNOR = r_LFSR[28] ^~ r_LFSR[25]; end 29: begin r_XNOR = r_LFSR[29] ^~ r_LFSR[27]; end 30: begin r_XNOR = r_LFSR[30] ^~ r_LFSR[6] ^~ r_LFSR[4] ^~ r_LFSR[1]; end 31: begin r_XNOR = r_LFSR[31] ^~ r_LFSR[28]; end 32: begin r_XNOR = r_LFSR[32] ^~ r_LFSR[22] ^~ r_LFSR[2] ^~ r_LFSR[1]; end endcase // case (NUM_BITS) end // always @ (*) assign o_LFSR_Data = r_LFSR[NUM_BITS:1]; // Conditional Assignment (?) assign o_LFSR_Done = (r_LFSR[NUM_BITS:1] == i_Seed_Data) ? 1'b1 : 1'b0;endmodule // LFSR





沒有留言:
張貼留言