HBLbits_Verilog Basic_Vectors
wire [99:0] my_vector; // Declare a 100-element vector assign out = my_vector[10]; // Part-select one bit out of the vector
//========================================
Declaring Vectors
wire [7:0] w; // 8-bit wire reg [4:1] x; // 4-bit reg output reg [0:0] y; // 1-bit reg that is also an output port (this is still a vector) input wire [3:-2] z; // 6-bit wire input (negative ranges are allowed) output [3:0] a; // 4-bit output wire. Type is 'wire' unless specified otherwise. wire [0:7] b; // 8-bit wire where b[0] is the most-significant bit.
//========================================Implicit nets
wire [2:0] a, c; // Two vectors assign a = 3'b101; // a = 101 assign b = a; // b = 1 implicitly-created wire assign c = b; // c = 001 <-- bug my_module i1 (d,e); // d and e are implicitly one-bit wide if not declared.
// This could be a bug if the port was intended to be a vector.
//========================================Unpacked vs. Packed Arrays
reg [7:0] mem [255:0]; // 256 unpacked elements, each of which is a 8-bit packed vector of reg. reg mem2 [28:0]; // 29 unpacked elements, each of which is a 1-bit reg.
//========================================Accessing Vector Elements: Part-Select
w[3:0] // Only the lower 4 bits of w x[1] // The lowest bit of x x[1:1] // ...also the lowest bit of x z[-1:-2] // Two lowest bits of z b[3:0] // Illegal. Vector part-select must match the direction of the declaration. b[0:3] // The *upper* 4 bits of b. assign w[3:0] = b[0:3]; // Assign upper 4 bits of b to lower 4 bits of w. w[3]=b[0], w[2]=b[1], etc.
//========================================module top_module(
input [2:0] vec,
output [2:0] outv,
output o2,
output o1,
output o0
);
assign outv = vec;
// This is ok too: assign {o2, o1, o0} = vec;
assign o0 = vec[0];
assign o1 = vec[1];
assign o2 = vec[2];
endmodule
input [2:0] vec,
output [2:0] outv,
output o2,
output o1,
output o0
);
assign outv = vec;
// This is ok too: assign {o2, o1, o0} = vec;
assign o0 = vec[0];
assign o1 = vec[1];
assign o2 = vec[2];
endmodule
A Bit of Practice
Build a combinational circuit that splits an input half-word (16 bits, [15:0] ) into lower [7:0] and upper [15:8] bytes.
module top_module(
input wire [15:0] in,
output wire [7:0] out_hi,
output wire [7:0] out_lo );
assign out_hi=in[15:8];
assign out_lo=in[7:0];
endmodule
A 32-bit vector can be viewed as containing 4 bytes (bits [31:24], [23:16], etc.). Build a circuit that will reverse the byte ordering of the 4-byte word.
AaaaaaaaBbbbbbbbCcccccccDddddddd => DdddddddCcccccccBbbbbbbbAaaaaaaa
module top_module(
input [31:0] in,
output [31:0] out );//
assign out[31:24] = in[7:0];
assign out[23:16] = in[15:8];
assign out[15:8] = in[23:16];
assign out[7:0] = in[31:24];
endmodule
Bitwise vs. Logical Operators
//let x = 4’b1010, y = 4’b0000 x | y //bitwise OR, result is 4’b1010 x || y //logical OR, result is 1
module top_module(
input [2:0] a,
input [2:0] b,
output [2:0] out_or_bitwise,
output out_or_logical,
output [5:0] out_not
);
assign out_or_bitwise= a | b;
assign out_or_logical= a || b;
assign out_not[5:3]= ~a;
assign out_not[2:0]= ~b;
endmodule
//===========================================module top_module(
input [2:0] a,
input [2:0] b,
output [2:0] out_or_bitwise,
output out_or_logical,
output [5:0] out_not
);
assign out_or_bitwise = a | b;
assign out_or_logical = a || b;
assign out_not[2:0] = ~a; // Part-select on left side is o.
assign out_not[5:3] = ~b; //Assigning to [5:3] does not conflict with [2:0]
endmodule
Build a combinational circuit with four inputs, in[3:0].
There are 3 outputs:
- out_and: output of a 4-input AND gate.
- out_or: output of a 4-input OR gate.
- out_xor: output of a 4-input XOR gate.
module top_module(
input [3:0] in,
output out_and,
output out_or,
output out_xor
);
assign out_and=in[0] & in[1] & in[2] & in[3] ;
assign out_or =in[0] | in[1] | in[2] | in[3] ;
assign out_xor=in[0] ^ in[1] ^ in[2] ^ in[3] ;
endmodule
{3'b111, 3'b000} => 6'b111000 {1'b1, 1'b0, 3'b101} => 5'b10101 {4'ha, 4'd10} => 8'b10101010 // 4'ha and 4'd10 are both 4'b1010 in binaryinput [15:0] in; output [23:0] out; assign {out[7:0], out[15:8]} = in; // Swap two bytes. Right side and left side are both 16-bit vectors. assign out[15:0] = {in[7:0], in[15:8]}; // This is the same thing. assign out = {in[7:0], in[15:8]}; // This is different. The 16-bit vector on the right is extended to // match the 24-bit vector on the left, so out[23:16] are zero. // In the first two examples, out[23:16] are not assigned.module top_module ( input [4:0] a, b, c, d, e, f, output [7:0] w, x, y, z );// assign {w,x,y,z} = { a, b, c, d, e, f,2'b11 }; endmoduleGiven an 8-bit input vector [7:0], reverse its bit ordering.module top_module( input [7:0] in, output [7:0] out ); assign out[7]=in[0]; assign out[6]=in[1]; assign out[5]=in[2]; assign out[4]=in[3]; assign out[3]=in[4]; assign out[2]=in[5]; assign out[1]=in[6]; assign out[0]=in[7]; endmoduleThe concatenation operator allowed concatenating together vectors to form a larger vector.Examples:
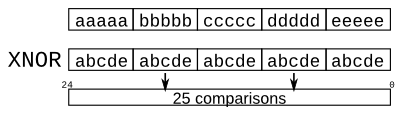
{5{1'b1}} // 5'b11111 (or 5'd31 or 5'h1f) {2{a,b,c}} // The same as {a,b,c,a,b,c} {3'd5, {2{3'd6}}} // 9'b101_110_110. It's a concatenation of 101 with // the second vector, which is two copies of 3'b110.Build a circuit that sign-extends an 8-bit number to 32 bits. This requires a concatenation of 24 copies of the sign bit (i.e., replicate bit[7] 24 times) followed by the 8-bit number itself.module top_module (input [7:0] in,output [31:0] out );// Concatenate two things together:// 1: {in[7]} repeated 24 times (24 bits)// 2: in[7:0] (8 bits)assign out = { {24{in[7]}}, in };endmoduleGiven five 1-bit signals (a, b, c, d, and e), compute all 25 pairwise one-bit comparisons in the 25-bit output vector. The output should be 1 if the two bits being compared are equal.
out[24] = ~a ^ a; // a == a, so out[24] is always 1. out[23] = ~a ^ b; out[22] = ~a ^ c; ... out[ 1] = ~e ^ d; out[ 0] = ~e ^ e;
module top_module (
input a, b, c, d, e,
output [24:0] out );//
// The output is XNOR of two vectors created by
// concatenating and replicating the five inputs.
assign out[24] = ~{a} ^ {a};
assign out[23] = ~{a} ^ {b};
assign out[22] = ~{a} ^ {c};
assign out[21] = ~{a} ^ {d};
assign out[20] = ~{a} ^ {e};
assign out[19] = ~{b} ^ {a};
assign out[18] = ~{b} ^ {b};
assign out[17] = ~{b} ^ {c};
assign out[16] = ~{b} ^ {d};
assign out[15] = ~{b} ^ {e};
assign out[14] = ~{c} ^ {a};
assign out[13] = ~{c} ^ {b};
assign out[12] = ~{c} ^ {c};
assign out[11] = ~{c} ^ {d};
assign out[10] = ~{c} ^ {e};
assign out[9] = ~{d} ^ {a};
assign out[8] = ~{d} ^ {b};
assign out[7] = ~{d} ^ {c};
assign out[6] = ~{d} ^ {d};
assign out[5] = ~{d} ^ {e};
assign out[4] = ~{e} ^ {a};
assign out[3] = ~{e} ^ {b};
assign out[2] = ~{e} ^ {c};
assign out[1] = ~{e} ^ {d};
assign out[0] = ~{e} ^ {e};
endmodule




沒有留言:
張貼留言