地球是半徑6370公里的龐大球體,自地表 山坡 山頂 建築物頂向自由空間輻射的電磁波一定會受到對流層(Troposphere) (14Km~18Km)內大氣層的影響發生吸收而衰減同時還有反射 折射 繞射 散射及多路徑傳播而使得接收信號產生衰落(Fading)現象。
1. 大氣吸收 : 大氣層內對電波吸收最有影響的就是 氧氣(Oxygen)與水蒸氣(Water Vapor) 如果工作頻率超過10GHz以上影響更嚴重。
水蒸氣在22.2GHz 及183.3GHz 影響嚴重
氧氣在56GHz~65GHz 及118.8GHz 影響嚴重
2.雨衰(Rain Attenuation)
根據Ryde理論如果工作頻率超過10GHz以上降雨產生的吸收而衰減影響頗大。 (有時比氧氣 水蒸氣的吸收更大)雨衰是衛星通信系統在 W/V 頻段運行的最重要的傳播損傷[4]。雨徑衰減由下式給出
3.大氣層折射(Atmospheric Refraction)
The refractive index of air
It can be simply demonstrated, based on the Debye theory of polar molecules, that refractivity can be calculated from pressure p (hPa) and temperature T (K) as (Brussaard, 1996):
where e (hPa) stands for a water vapour pressure that is related to the relative humidity H (%) by a relation:
where e
where for the saturation vapour above liquid water a = 6.1121 hPa, b = 17.502 and c = 240.97º C and above ice a = 6.1115 hPa, b = 22.452 and c = 272.55º C.
It is seen in Fig.1a where the dependence of the refractivity on temperature and relative humidity is depicted that refractivity generally increases with humidity. Its dependence on temperature is not generally monotonic however. For humidity values larger than about 40%, refractivity also increases with temperature.
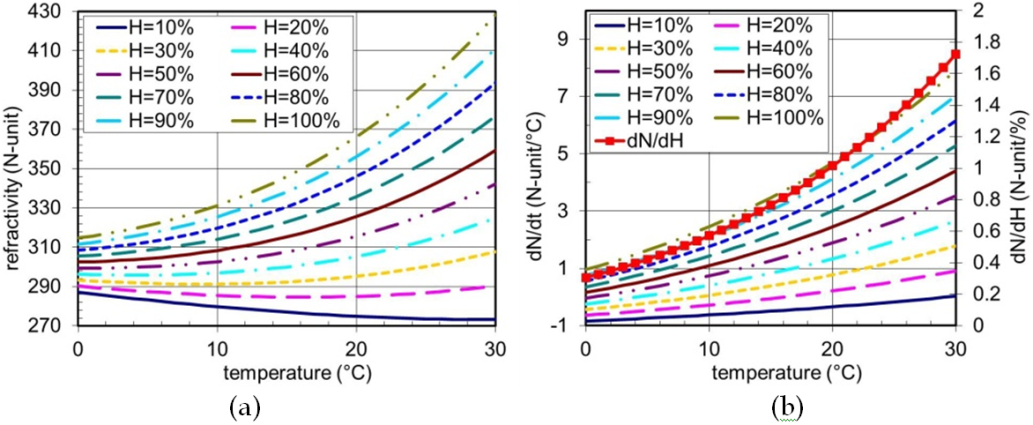
Figure 1.
The radio refractivity dependence on temperature and relative humidity of air for pressure
The sensitivity of refractivity on temperature and relative humidity of air is shown in Fig. 1b. For t = 10º C (cca average near ground temperature in the Czech Republic), H = 70% (cca average near ground relative humidity) and p = 1000 hPa, the sensitivities are dN/dt = 1.43 N-unit/ºC, dN/dH = 0.57 N-unit/% and dN/dp = 0.27 N-unit/hPa. The refractivity variation is usually most significantly influenced by the changes of relative humidity as a water vapour content often changes rapidly (both in space and time) and it is least sensitive to pressure variation. However a decrease in pressure with altitude is mainly responsible for a standard vertical gradient of the atmospheric refractivity.
During standard atmospheric conditions, the temperature and pressure are decreasing with the height above the ground with lapse rates of about 6º C/km and 125 hPa/km (near ground gradients). Assuming that relative humidity is approximately constant with height, a standard value of the lapse rate of refractivity with a height h can be obtained using pressure and temperature sensitivities and their standard lapse rates. Such an estimated standard vertical gradient of refractivity is about dN/dh ≈ -42 N-units/km. It will be seen that such value is very close to the observed long term median of the vertical gradient of refractivity.
4.路徑剖面圖 (Path Profile)
地球表面高低起伏不同有平原 高山 建築物 湖泊 森林等分布 為了了解電波傳播的路線 常用K=4/3 的路徑剖面圖。














沒有留言:
張貼留言